A curette is a special tool used in various medical procedures, especially in surgeries or medical exams. The tool is used to remove tissue, scrape surfaces, or collect samples from different parts of the body.
What Is a Curette?
A curette is a small, hand-held surgical instrument with a scoop, ring, or spoon-like tip. The primary function of a curette is to scrape or remove tissue from the body.
It is commonly used in surgeries, dental procedures, gynecology, and other medical practices. A curette allows the doctor or surgeon to gently remove or clean the area without causing too much damage to surrounding tissue.
In some cases, curettes are used to collect tissue for biopsy, remove dead or infected tissue, or clean a surgical site. The design of the curette makes it ideal for delicate work, and it is available in different shapes to suit different tasks.
Why Is a Curette Important?
Curettes are essential tools in many medical fields. They allow doctors to perform precise and controlled procedures. Whether it’s scraping tissue during a dental cleaning, removing a sample for a biopsy, or cleaning the uterine lining after a miscarriage, the curette plays an important role in patient care.
The importance of using the right curette cannot be overstated. Using the wrong type of curette could lead to complications, pain, or improper treatment. Therefore, understanding the different types of curettes and their uses is vital for healthcare providers.
Types of Curette
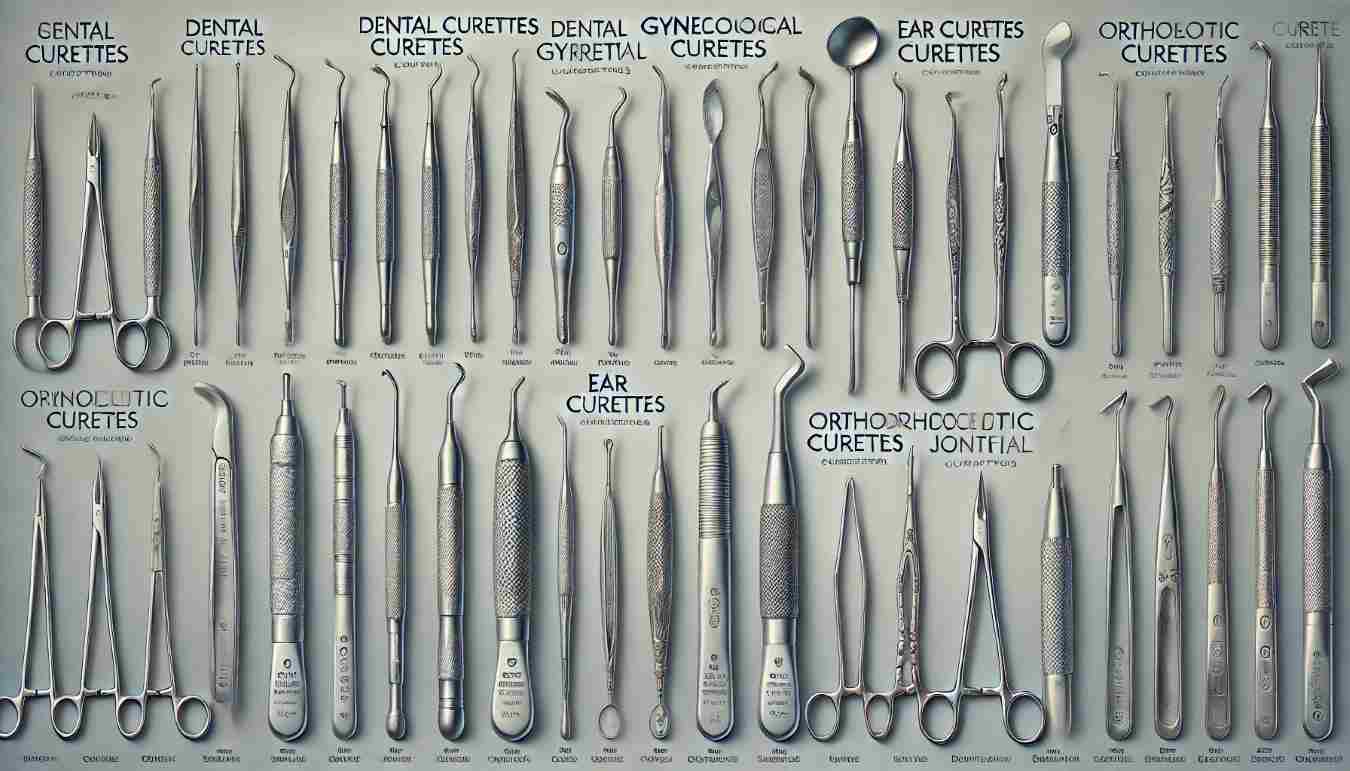
There are several types of curettes, each designed for specific tasks in different medical fields. Let’s explore the most common types:
1. Dental Curettes
Dental curettes are specialized for use in dental procedures. They have sharp, curved tips that allow the dentist to remove plaque, tartar, and debris from the teeth and gums. These curettes are designed to be gentle yet effective at cleaning hard-to-reach areas in the mouth.
Dental curettes come in various shapes, such as straight or curved, and may have different angles to allow the dentist to access different parts of the mouth. Some curettes are designed for use in the cleaning of periodontal pockets, which are spaces between the teeth and gums that can harbor bacteria.
2. Gynecological Curettes
Gynecologists use curettes to perform procedures like dilation and curettage (D&C). A D&C is a medical procedure where tissue is scraped from the inside of the uterus. This is typically done to remove any abnormal tissue, like a miscarriage, or to sample the tissue for examination.
Gynecological curettes are usually long and slender, allowing the physician to reach deep into the uterus. They can have a spoon-shaped, ring-shaped, or sharp-edged tip, depending on the specific procedure. For example, a curette with a sharp edge is often used for more invasive procedures that require the scraping of uterine tissue.
3. Ear Curettes
An ear curette is a small instrument designed for cleaning the ears. The curette typically has a loop, spoon, or hook shape at the tip, which is used to carefully remove earwax or foreign bodies from the ear canal. The tool is usually made from metal or plastic, depending on the intended use.
Ear curettes are commonly used by healthcare providers during ear exams, but they can also be used by patients at home. However, it’s important to note that ear curettes should be used with caution, as inserting them too deeply into the ear canal can cause damage to the delicate ear structures.
4. Orthopedic Curettes
Orthopedic curettes are used in surgeries related to bones and joints. These curettes are designed to remove damaged tissue or bone fragments from a joint or surgical site. They can also be used to scrape out infected tissue from a bone or joint during procedures like joint replacement surgeries.
The orthopedic curette may have a rounded or spoon-shaped tip to help scrape tissue without causing excessive trauma to surrounding healthy tissue. These curettes are often used in conjunction with other surgical tools to clean and prepare the surgical site for treatment.
5. Curettes for Dermatological Procedures
In dermatology, curettes are used to remove growths, skin tags, warts, or other abnormal tissue from the skin. Dermatological curettes have sharp tips that allow the doctor to carefully scrape away these tissues while preserving the surrounding skin.
A dermatological curette often has a small, spoon-like or ring-shaped tip, and some are designed with a handle that helps the practitioner maintain control during the procedure. These curettes are essential for removing benign growths and can be used in both minor skin procedures and more involved dermatological surgeries.
Choosing the Right Curette
When selecting the right curette, there are several factors to consider:
Purpose of Use: Different curettes are designed for different purposes. For example, a dental curette is unsuitable for use in gynecological procedures. Knowing the type of procedure and the area being treated will help determine the appropriate curette.
Shape and Size of the Tip: Curettes come in various shapes, including spoon shaped, ring-shaped, and flat-edged. The tip’s size and design depend on the specific task. For instance, a larger tip is typically used for scraping large areas, while a smaller tip is ideal for delicate or precise work.
Material: Curettes are made from a variety of materials, including stainless steel, plastic, and even ceramic. Stainless steel is often preferred because of its strength, durability, and ability to be sterilized.
Handle Design: Some curettes have longer handles for use in deeper areas, while others have shorter handles for better control in surface-level procedures. Consider the length of the handle and the comfort of the grip when selecting a curette for a specific task.
Sterility and Maintenance: Sterilization is important for any surgical instrument, including curettes. Choose curettes that are easy to clean and maintain. Stainless steel curettes are often preferred as they can be autoclaved and sterilized more easily.
How Curettes Are Used in Medical Procedures
Curettes are typically used to remove or scrape tissue in a controlled, precise manner. During medical procedures, a doctor or surgeon will carefully insert the curette into the area to be treated. For example, during a D&C procedure, a gynecologist may use a curette to scrape the lining of the uterus.
When performing dental cleanings, a dentist will use a curette to remove tartar and plaque from the teeth and gum line. In dermatology, a curette is used to scrape away abnormal skin tissue, such as warts or precancerous growths.
The key to using a curette effectively is understanding the anatomy of the area being treated and selecting the right type of curette for the job.
FAQs
1. What is a curette?
A curette is a small, scoop-shaped surgical instrument used for scraping or debriding biological tissue in medical and dental procedures.
2. What are curettes used for?
Curettes are utilized to remove tissue, scrape surfaces, or collect samples from various parts of the body, including the uterus, teeth, and skin.
3. What are the different types of curettes?
There are several types of curettes, including:
Dental Curettes: Used in dentistry to remove plaque, tartar, and debris from teeth and gums.
Gynecological Curettes: Employed in procedures like dilation and curettage (D&C) to remove tissue from the uterus.
Ear Curettes: Designed to clean the ear canal by removing earwax or foreign bodies.
Orthopedic Curettes: Used in bone and joint surgeries to remove damaged tissue or bone fragments.
Dermatological Curettes: Utilized to excise skin growths, warts, or abnormal tissue from the skin.
4. How do curettes differ from other surgical instruments?
Curettes have a scoop, ring, or spoon-shaped tip, making them ideal for scraping or debriding tissue. This design allows for precise removal of tissue with minimal damage to surrounding areas.
5. Are curettes reusable?
Yes, most curettes are made from stainless steel and can be sterilized and reused. However, some disposable curettes are also available for single-use to prevent cross-contamination.
6. What precautions should be taken when using a curette?
Proper training in the use of curettes is essential to avoid injury to the patient or the practitioner. Additionally, ensuring that the curette is sterile before use is crucial to prevent infections.
7. Can curettes be used at home?
While some ear curettes are available for home use to remove earwax, it’s important to use them cautiously. Inserting a curette too deeply into the ear canal can cause damage. It’s advisable to consult a healthcare professional before attempting to use a curette at home.
8. How should curettes be cleaned and sterilized?
Curettes should be cleaned thoroughly to remove any tissue or debris. They should then be sterilized using appropriate methods, such as autoclaving, to ensure they are safe for reuse.
9. Are there any risks associated with curettage procedures?
Yes, potential risks include infection, bleeding, or damage to nearby organs. It’s important to discuss these risks with a healthcare provider before undergoing any procedure involving curettage.
10. How can I learn more about using curettes safely?
If you’re a healthcare professional, seek training and guidance from experienced practitioners and reputable medical sources. Always follow established protocols and guidelines when using curettes in clinical settings.