Navigator Pear: A Comprehensive Guide to Cultivation, Benefits, and Uses
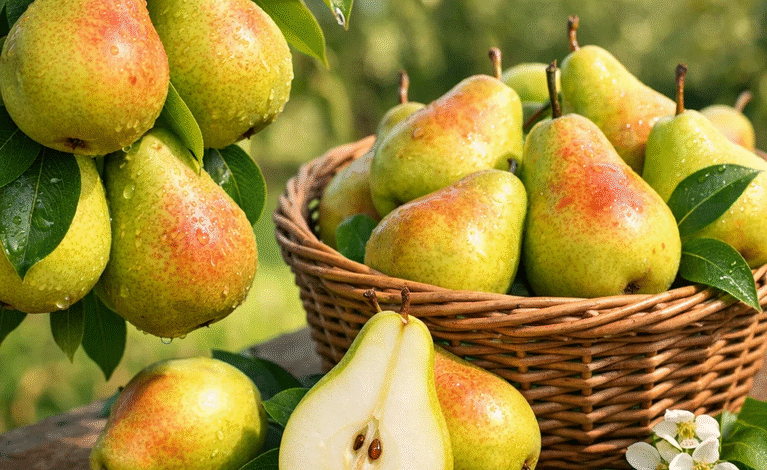

Navigator pear is one of the most remarkable and versatile pear varieties, celebrated for its sweet flavor, crisp texture, and nutritional value. Its adaptability and high-quality fruit make it a favorite among gardeners, commercial orchards, and pear enthusiasts worldwide. In this guide, we explore everything about navigator pear, including its history, cultivation techniques, nutritional profile, health benefits, storage tips, and practical uses. Whether you are a professional grower or a home gardener, understanding the characteristics and potential of navigator pear can enhance your appreciation for this exceptional fruit.
Introduction: Why Navigator Pear Stands Out
The navigator pear has gained popularity in recent years due to its unique combination of flavor, productivity, and resilience. Unlike some pear varieties that are susceptible to pests or disease, the navigator pear demonstrates strong resistance and adaptability to different climates. Its sweet, juicy flesh and slightly granular texture make it ideal for fresh consumption, cooking, and preserving.
Gardeners and orchard managers often choose navigator pear for its consistent yield, extended harvest season, and long shelf life. Beyond its practical advantages, the fruit also offers nutritional benefits, including dietary fiber, vitamins, and antioxidants, making it a healthy choice for families and individuals seeking natural sources of essential nutrients.
Origins and History of Navigator Pear
The navigator pear is a hybrid variety developed to combine hardiness with superior fruit quality. Breeders focused on producing a pear that could thrive in diverse climates while maintaining excellent flavor. Over the decades, navigator pear has become widely cultivated in temperate regions, gaining recognition for its reliable harvests and disease resistance.
This variety has been particularly popular in commercial orchards because it balances productivity with market appeal. The medium-to-large size, attractive yellow-green skin, and smooth texture have made it a preferred choice for both fresh markets and culinary use. Its adaptability to different soil types further underscores why it has become a staple in pear cultivation.
Key Characteristics of Navigator Pear
Understanding the physical and botanical traits of navigator pear is crucial for successful cultivation. Here are some key characteristics:
- Fruit Size and Appearance: Medium to large, typically round or slightly elongated, with yellow-green skin that may develop a subtle blush.
- Texture and Taste: Juicy, sweet, and mildly granular, offering a balance of firmness and tenderness.
- Harvest Season: Usually mid-to-late season, providing an extended period for collection and sale.
- Tree Growth: Medium-sized trees with dense foliage, suitable for both home gardens and commercial orchards.
- Resilience: Moderate resistance to common pear diseases such as fire blight and powdery mildew.
These traits make navigator pear an appealing choice for growers seeking a reliable, high-quality fruit with multiple uses.
Nutritional Profile of Navigator Pear
The navigator pear is not only delicious but also nutritionally rich, making it a smart addition to any diet. A single medium-sized pear contains:
- Dietary fiber – supports healthy digestion and helps regulate blood sugar.
- Vitamin C – boosts immunity and promotes skin health.
- Potassium – aids in heart health and fluid balance.
- Antioxidants – help protect cells from oxidative stress.
Low in calories and naturally hydrating, navigator pear provides a nutritious snack that is both satisfying and beneficial for overall health. Incorporating this fruit into daily meals can contribute to heart health, weight management, and digestive wellness.
Growing Navigator Pear: Essential Tips
Growing navigator pear successfully requires attention to soil, sunlight, watering, and pruning. Here are some essential tips for cultivating healthy trees:
1. Soil Requirements
Navigator pear trees thrive in well-drained, fertile soils with a slightly acidic to neutral pH. Loamy soils enriched with organic matter provide optimal conditions for root development. Avoid waterlogged or overly compacted soil, as it may hinder growth and increase disease susceptibility.
2. Sunlight and Planting Location
Full sunlight is essential for navigator pear. Choose a location that receives at least 6–8 hours of direct sunlight per day, ensuring proper fruit development and enhanced sugar content.
3. Watering and Irrigation
Consistent watering is crucial, especially during dry spells and fruit development stages. Use deep, infrequent watering to encourage deep root growth and reduce stress on the tree. Mulching around the base helps retain moisture and suppress weeds.
4. Pruning and Maintenance
Pruning helps maintain tree shape, encourages air circulation, and improves fruit quality. Remove dead, damaged, or overcrowded branches annually to promote healthy growth and reduce disease risk.
Pollination and Yield Considerations
Navigator pear is partially self-fertile but benefits from cross-pollination with compatible pear varieties. This improves fruit set, size, and overall yield. Bees and other pollinators play a crucial role in ensuring effective pollination, so maintaining a pollinator-friendly environment is essential.
On average, a healthy navigator pear tree can produce 50–150 pounds of fruit annually, depending on age, soil quality, and care practices. Regular monitoring, fertilization, and pest management help maximize yield and ensure consistent harvests.
Common Pests and Diseases
While navigator pear is moderately resistant to many diseases, growers should remain vigilant against common issues:
- Fire Blight: Bacterial infection causing blackened leaves and branches. Proper pruning and resistant rootstocks reduce the risk.
- Codling Moth: Larvae that burrow into fruit; controlled through monitoring and pheromone traps.
- Pear Scab: Fungal infection causing leaf and fruit blemishes; managed with fungicide applications and proper airflow.
Regular inspection, proper sanitation, and timely interventions are key to maintaining healthy trees and high-quality fruit.
Harvesting and Storage
Harvesting navigator pear at the right time ensures optimal flavor and shelf life. Key tips include:
- Timing: Pick pears when they have reached full size and color but are still firm. Unlike some fruits, pears often ripen off the tree, so post-harvest ripening is normal.
- Handling: Handle fruit gently to prevent bruising. Use padded containers for transport and storage.
- Storage Conditions: Store in a cool, humid environment (32–35°F) to extend shelf life. Proper storage can keep navigator pear fresh for several weeks.
Correct harvesting and storage practices preserve quality, flavor, and nutritional value for consumers or personal use.
Culinary Uses of Navigator Pear
The navigator pear is versatile in culinary applications due to its sweet, juicy flavor and firm texture. Popular uses include:
- Fresh Consumption: Ideal as a snack or in fruit salads.
- Baking and Cooking: Excellent for pies, tarts, crisps, and poached dishes.
- Preserves and Sauces: Can be made into jams, chutneys, or purees.
- Beverages: Used in smoothies, juices, or infused waters.
Its ability to maintain texture during cooking makes navigator pear a preferred choice for both home chefs and professional kitchens.
Health Benefits of Navigator Pear
Including navigator pear in the diet offers several health advantages:
- Digestive Health: High dietary fiber supports bowel regularity and gut health.
- Heart Health: Potassium and antioxidants contribute to cardiovascular wellness.
- Immune Support: Vitamin C and other micronutrients enhance immune function.
- Weight Management: Low-calorie content and fiber-rich flesh promote satiety.
Regular consumption can complement a balanced diet and promote overall well-being.
Tips for Home Gardeners
For individuals growing navigator pear at home, consider these additional tips:
- Spacing: Plant trees with adequate spacing to allow sunlight penetration and airflow.
- Fertilization: Use balanced fertilizers annually to encourage healthy growth and fruiting.
- Pest Control: Implement organic or chemical controls as necessary while monitoring tree health.
- Support Structures: Use stakes or trellises for young trees to support growth and prevent wind damage.
These practices ensure a successful harvest and long-term tree health.
Conclusion
Navigator pear is a highly adaptable, flavorful, and nutritious pear variety that offers significant benefits for both growers and consumers. From its resilient growth characteristics and high yield to its culinary versatility and health benefits, navigator pear stands out as an exceptional choice for orchards, home gardens, and commercial use. Proper cultivation, pollination, and storage practices enhance fruit quality, while its nutritional content makes it a valuable addition to any diet. Whether eaten fresh, cooked, or preserved, navigator pear combines taste, practicality, and health, making it a pear variety worth growing and enjoying.
FAQs
1. What is navigator pear?
Navigator pear is a hybrid pear variety known for its sweet, juicy flavor, firm texture, and adaptability to different growing conditions.
2. When is the best time to harvest navigator pear?
Harvest in mid-to-late season when the fruit has reached full size and color but remains firm. Pears can ripen off the tree.
3. Can navigator pear grow in home gardens?
Yes. It adapts well to temperate climates and can thrive in home orchards with proper care.
4. What are common pests affecting navigator pear?
Fire blight, codling moth, and pear scab are common pests and diseases that can affect navigator pear trees.
5. How should navigator pear be stored?
Store in a cool, humid environment (32–35°F) to extend shelf life and maintain quality.
6. Is navigator pear good for health?
Yes. It is high in fiber, vitamins, potassium, and antioxidants, supporting digestive, heart, and immune health.
7. What are the culinary uses of navigator pear?
It can be eaten fresh, used in baking, cooked into sauces, preserves, or added to beverages and smoothies.
Get more updates or Stories on Next Magazine