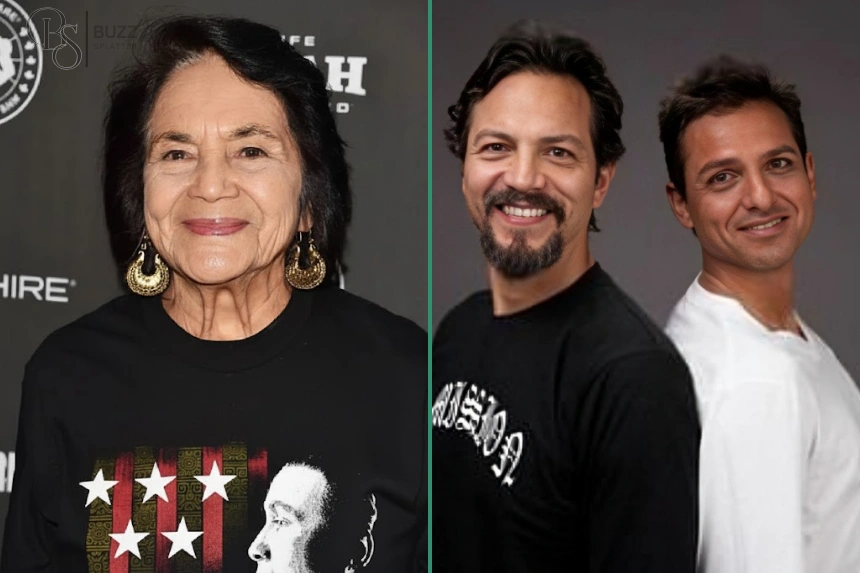
Eldy Banda Biography: Nurse, Activist, and Mother of Benjamin Bratt

Eldy Banda is a remarkable woman whose life story reflects courage, compassion, and cultural pride. Best known as the mother of acclaimed actor Benjamin Bratt, she forged an identity far beyond that association. A Peruvian-born immigrant, dedicated nurse, passionate activist, and influential film producer, Eldy Banda devoted her life to service, social justice, and family. Her journey from Lima, Peru, to the heart of American civil rights movements stands as a testament to resilience, empathy, and the enduring power of lived values.
| Field | Details |
|---|---|
| Full Name | Eldy Banda |
| Known For | Nurse, Social justice activist, Film producer |
| Famous As | Mother of actor Benjamin Bratt |
| Date of Birth | March 22, 1940 |
| Birthplace | Lima, Peru |
| Nationality | Peruvian-American |
| Ethnicity | Latina (Peruvian) |
| Religion | Not publicly disclosed |
| Profession | Registered nurse, Activist, Documentary producer |
| Years Active | 1960s–1990s |
| Education | Nursing training in the United States (institution not publicly disclosed) |
| Notable Activism | 1969 Alcatraz Island occupation, Native American rights advocacy |
| Film Work | Producer of “Follow Me Home” (1996) |
| Marital Status | Married |
| Spouse | Peter Bratt Sr. (m. 1960) |
| Children | Five children, including Benjamin Bratt and Peter Bratt Jr. |
| Son (Notable) | Benjamin Bratt (Actor, born December 16, 1963) |
| Other Children | Peter Bratt Jr. (Filmmaker) and three others (names private) |
| Parents | Not publicly disclosed |
| Siblings | Not publicly disclosed |
| Residence | San Francisco, California, USA |
| Languages | Spanish, English |
| Notable Traits | Resilient, compassionate, community-oriented |
| Legacy | Advocacy for Indigenous rights, immigrant empowerment, cultural representation |
Early Life and Childhood in Peru
Eldy Banda was born on March 22, 1940, in Lima, Peru, into a culturally rich environment deeply connected to music, family traditions, and communal values. From an early age, she demonstrated exceptional artistic ability, particularly in singing and playing musical instruments. Music was not merely a hobby but a shared family language that strengthened bonds and shaped her emotional intelligence.
Growing up in mid-20th-century Peru, Eldy was immersed in a society where heritage and storytelling played vital roles. Family gatherings often revolved around music and conversation, instilling in her a sense of belonging and cultural pride. These early years fostered resilience and adaptability, qualities that would later define her journey as an immigrant and activist. Her Peruvian upbringing laid the foundation for lifelong empathy and cultural awareness.

Eldy Banda Biography
Family Influence and Cultural Foundations
Eldy Banda’s formative years were shaped by strong family values emphasizing perseverance, respect, and community support. While details about her parents and siblings remain private, it is evident that her household encouraged creativity and independence. The encouragement she received to explore music and expression nurtured confidence and self-discipline.
This environment also instilled a deep understanding of social responsibility. Witnessing inequality and hardship in her surroundings awakened a sensitivity to injustice. These early impressions later translated into activism in the United States, where she aligned her immigrant experiences with broader struggles for Indigenous and minority rights. Her Peruvian roots remained a moral compass throughout her life.
Immigration to the United States
In the 1950s, at just 14 years old, Eldy Banda immigrated to the United States, settling in San Francisco, California. This life-altering decision marked the beginning of a challenging yet transformative chapter. Leaving Peru required emotional strength, as she navigated unfamiliar customs, language barriers, and economic uncertainty.
San Francisco, with its progressive ideals and cultural diversity, offered both opportunity and challenge. Eldy embraced the city’s energy while confronting the realities faced by young immigrants. She balanced ambition with adaptation, gradually building a sense of belonging. Her immigration story mirrors that of many newcomers who reshape their identities while contributing profoundly to their adopted communities.
Adjusting to Life as an Immigrant
The transition to American life demanded resilience. Eldy Banda faced linguistic challenges, cultural dissonance, and financial hardship, yet she persisted with determination. She worked tirelessly, learning to navigate institutions and social systems that were initially foreign to her.
These struggles strengthened her empathy for marginalized communities. As she found her footing, Eldy became increasingly aware of systemic inequalities affecting immigrants, Indigenous people, and people of color. This awareness later fueled her activism and informed her professional choices. San Francisco became not just a home but a platform from which she would serve others.
Career Path and Calling as a Nurse
Eldy Banda found her professional calling in nursing, a field that perfectly aligned with her compassionate nature. After completing her training in the United States, she began working in San Francisco’s healthcare system, dedicating decades to patient care. Nursing allowed her to serve diverse populations, many of whom faced barriers to medical access.
Her work extended beyond clinical responsibilities. Eldy practiced holistic care, recognizing emotional and cultural needs alongside physical health. Long shifts and emotional demands never deterred her commitment. She became known for her warmth, professionalism, and advocacy for underserved patients, embodying healthcare as both service and justice.
Impact and Legacy in Nursing
Throughout her nursing career, Eldy Banda touched countless lives, offering comfort and dignity to patients from all walks of life. She advocated quietly but persistently for equitable healthcare, particularly for immigrant and low-income communities. Colleagues respected her for her work ethic and empathy.
She also mentored younger nurses, emphasizing resilience, cultural sensitivity, and compassion. For Eldy, nursing was not merely a profession but a vocation grounded in humanity. Her legacy in healthcare reflects how one individual can elevate everyday work into meaningful social contribution.
Awakening to Activism and Social Justice
Eldy Banda’s personal experiences as an immigrant naturally evolved into a broader commitment to social justice activism. Living in San Francisco during the civil rights era exposed her to movements advocating equality, Indigenous sovereignty, and community empowerment. She felt a deep resonance with these causes.
Her activism was rooted in lived experience rather than ideology alone. Eldy recognized parallels between the struggles of Native American communities and the marginalization faced by immigrants and minorities. This awareness propelled her into active participation in protests, rallies, and community organizing.
Role in the 1969 Alcatraz Occupation
One of the most defining moments in Eldy Banda’s activist life was her involvement in the 1969 occupation of Alcatraz Island. This historic protest, led by Native American activists, sought to reclaim Indigenous land and draw attention to systemic injustices. Eldy actively supported the movement and brought her young son, Benjamin Bratt, who was just five years old at the time.
This experience profoundly shaped her children’s worldview. By integrating activism into family life, Eldy demonstrated that social responsibility was not separate from everyday living. Her presence at Alcatraz symbolized solidarity across cultures and reinforced her lifelong commitment to justice.
Advocacy Beyond Alcatraz
Eldy Banda’s activism extended beyond a single event. She remained engaged in Native American rights, educational advocacy, and community empowerment initiatives. She collaborated with grassroots organizations, attended rallies, and supported policy discussions aimed at improving conditions for marginalized groups.
Her approach emphasized education and dialogue. Eldy believed sustainable change required awareness and empathy. She mentored young activists and encouraged civic engagement, especially among her children. Her activism was not performative but deeply personal, woven into her identity as a mother, nurse, and immigrant.
Transition Into Film and Cultural Storytelling
Later in life, Eldy Banda expanded her advocacy into filmmaking, recognizing storytelling as a powerful tool for social change. She served as producer of the documentary “Follow Me Home” (1996), directed by her son Peter Bratt Jr. The film explored themes of identity, racism, and belonging within American society.
Premiering at the Sundance Film Festival, the documentary received widespread acclaim and won the Audience Award for Best Feature Film at the San Francisco International Film Festival. Eldy’s involvement reflected her ability to translate activism into cultural narratives that reached broader audiences.
Significance of “Follow Me Home”
“Follow Me Home” mirrored Eldy Banda’s values, highlighting multicultural experiences and systemic inequality. As a producer, she navigated an industry where women of color were underrepresented, demonstrating strategic vision and perseverance. The film sparked conversations about race, identity, and community responsibility.
Her contribution extended beyond logistics; Eldy shaped the film’s moral compass. This venture solidified her role as a cultural influencer, bridging healthcare, activism, and media. It also reinforced the importance of intergenerational collaboration within her family.
Eldy Banda’s Family Background and Relatives
Family remained the cornerstone of Eldy Banda’s life. In 1960, she married Peter Bratt Sr., a sheet metal worker, in San Francisco. Their marriage was built on mutual respect, shared values, and commitment to raising socially conscious children. Peter Sr. provided stability and unwavering support throughout Eldy’s demanding career and activism.
Together, they raised five children, fostering a household rich in cultural pride, political awareness, and creativity. Eldy and Peter Sr. emphasized education, empathy, and community engagement, values that shaped each child’s path.
Children and Their Achievements
Among Eldy Banda’s children, Benjamin Bratt stands as the most publicly recognized. Born on December 16, 1963, he became an Emmy-nominated actor, known for roles in “Law & Order,” “Miss Congeniality,” and “Traffic.” Benjamin has frequently credited his mother for instilling social awareness and grounding him amid Hollywood success.
Another son, Peter Bratt Jr., emerged as a respected filmmaker and activist, directing socially conscious films including “Follow Me Home.” Eldy’s other children, though less publicly visible, have pursued meaningful paths influenced by her values. Details about extended relatives and Eldy’s parents remain respectfully private.
Influence on Benjamin Bratt’s Life and Career
Eldy Banda’s influence on Benjamin Bratt is profound and enduring. From early childhood, she exposed him to activism, cultural pride, and empathy. The Alcatraz occupation left a lasting impression, shaping his understanding of injustice and representation.
Benjamin has often spoken about his mother’s strength, crediting her for his grounded perspective and choice of socially meaningful roles. Her example encouraged him to embrace his heritage and advocate for diversity in film. Eldy’s legacy is deeply woven into his personal and professional identity.
Personal Challenges and Triumphs
Eldy Banda’s life was not without hardship. Immigration, professional discrimination, and the demands of balancing motherhood, nursing, and activism tested her resilience. She faced systemic barriers as a woman of color in multiple fields, from healthcare to filmmaking.
Yet, her triumphs were equally significant. Raising five children, sustaining a long marriage, succeeding in nursing, and producing an award-winning film reflect extraordinary perseverance. Eldy transformed challenges into opportunities for growth, mentoring others through example rather than rhetoric.
Cultural Impact and Broader Legacy
Eldy Banda’s cultural impact extends across healthcare, activism, and media. She bridged her Peruvian heritage with American social movements, enriching dialogues on identity and justice. Her involvement in Native American rights emphasized solidarity beyond ethnic boundaries.
Her life story continues to inspire immigrants, activists, and caregivers. Eldy represents how ordinary professions, when guided by purpose, can yield extraordinary influence. Her legacy is preserved through her children’s work and the communities she served.
Later Life and Enduring Influence
In her later years, Eldy Banda remained a respected figure within her family and community. While maintaining privacy, she continued to inspire through her lived example. Her story is often shared in discussions of activism, representation, and immigrant resilience.
Eldy’s influence persists not through headlines but through values passed down generations. Her life demonstrates that advocacy begins at home and radiates outward, shaping culture in lasting ways.
Conclusion
Eldy Banda’s life is a powerful narrative of courage, compassion, and conviction. From her birth in Lima, Peru, to her roles as a nurse, activist, film producer, and devoted mother, she exemplified purpose-driven living. Her influence on Benjamin Bratt and her broader contributions to social justice underscore the impact of one determined individual. Eldy Banda’s legacy reminds us that true change is built through service, empathy, and unwavering integrity.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Who is Eldy Banda?
Eldy Banda is a Peruvian-born nurse, social justice activist, film producer, and the mother of actor Benjamin Bratt.
When and where was Eldy Banda born?
She was born on March 22, 1940, in Lima, Peru.
What is Eldy Banda known for?
She is known for her nursing career, Native American rights activism, and producing the documentary “Follow Me Home.”
What was Eldy Banda’s role in the Alcatraz occupation?
She actively supported the 1969 Alcatraz Island occupation, advocating for Indigenous land rights.
Who was Eldy Banda married to?
She married Peter Bratt Sr. in 1960, and they raised five children together.
How did Eldy Banda influence Benjamin Bratt?
She instilled values of activism, cultural pride, and empathy, shaping his personal and professional life.
Did Eldy Banda work in film?
Yes, she was a producer of the award-winning documentary “Follow Me Home” (1996).
Get more updates or Stories on Next Magazine